The cost of sales for a software company involves direct expenses like development, infrastructure, support, and licensing, which are essential for profitability and effective pricing.
In this article, we’ll explore what the cost of sales entails for software companies, what it includes, and why it’s critical for accurate financial reporting and better decision-making.
What is Cost of Sales for a Software Company?
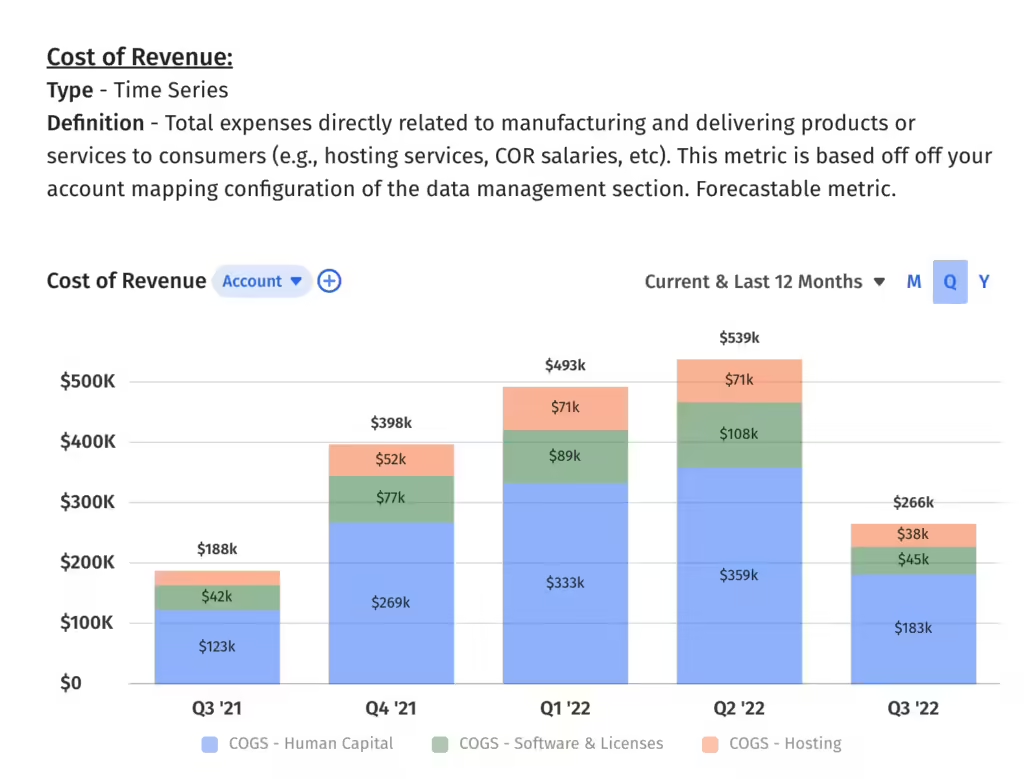
In the context of a software company, cost of sales (also known as COGS) represents the direct expenses tied to the delivery of software products or services to customers. These costs are necessary to produce, support, and distribute the software.
Unlike companies selling physical goods, software companies do not incur expenses like raw materials or manufacturing costs. Instead, the cost of sales for a software company typically includes software development costs, infrastructure, cloud services, customer support, licensing, and other operational expenses directly associated with delivering the product.
The cost of sales is a critical component in calculating a company’s gross profit. By subtracting the cost of sales from the company’s revenue, businesses can determine the amount of money made after covering the direct costs of producing and delivering the software.
Why is Cost of Sales Important?
The cost of sales plays a central role in determining profitability. For a software company, keeping an eye on cost of sales is essential for several reasons:
- Understanding Gross Profit: Gross profit is calculated by subtracting the cost of sales from total revenue. It indicates the efficiency of your company’s core operations in generating profit. A lower cost of sales typically results in a higher gross profit.
- Improving Pricing Strategy: An accurate calculation of the cost of sales allows software companies to set competitive and profitable prices for their products. Knowing how much it costs to deliver software to customers helps businesses avoid underpricing or overpricing.
- Cost Management: By identifying and analyzing the cost of sales, companies can identify areas where costs can be reduced or optimized. Whether it’s streamlining cloud hosting services, cutting down on unnecessary licensing fees, or optimizing support operations, managing these costs leads to greater efficiency and profitability.
- Investor Insights: Investors and stakeholders often look closely at the cost of sales to assess a company’s financial health. A company with well-managed and efficient cost control measures is more attractive to investors, as it suggests sustainability and potential for growth.
Key Components of Cost of Sales for a Software Company:
To fully understand the cost of sales, it’s essential to know what it comprises. The elements of the cost of sales for a software company can vary depending on the type of software being produced and the company’s business model, but the following components are common:
Software Development Costs:
The development of software is at the core of any software company’s operations. The costs associated with development are considered part of the cost of sales. This includes:
- Salaries for developers, engineers, and product managers: These are the individuals responsible for designing, developing, coding, testing, and maintaining the software.
- Development tools and platforms: The cost of purchasing or subscribing to development tools, software libraries, or third-party APIs essential for product creation.
- Third-party integrations: Many software products rely on other tools or APIs, and integrating them into your product often requires licensing fees or one-time payments.
Also Read: How To Disable Keys On Womier Software – A Complete Step-by-Step Guide!
Why Are These Costs Critical?
Software development is an ongoing process, especially for companies offering cloud-based solutions or subscription models like Software as a Service (SaaS). Continuous improvement, bug fixes, and updates are necessary to maintain competitiveness, user satisfaction, and security, making development one of the most significant components of the cost of sales.
Infrastructure and Hosting Costs:
For companies that provide cloud-based or SaaS products, infrastructure and hosting fees are a considerable portion of their cost of sales. These include:
- Cloud hosting costs: Expenses for hosting software on cloud providers such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud, or Microsoft Azure.
- Server maintenance: The cost of running servers, maintaining uptime, and ensuring scalability as demand increases.
- Data storage and transfer: Charges related to storing large amounts of data and facilitating data transfer between users and your platform.
Why Are These Costs Important?
Cloud-based solutions rely heavily on robust, reliable infrastructure to ensure seamless user experiences. Any downtime can result in dissatisfied customers, loss of revenue, or even legal liabilities. Hence, allocating resources to reliable infrastructure is a must for maintaining customer satisfaction and ensuring product reliability.
Customer Support and Service Costs:
For most software companies, customer support is crucial for ensuring a smooth experience for users. Support teams help with installation, troubleshooting, and resolving technical issues. Key support costs include:
- Salaries of support staff: Individuals who handle customer inquiries, technical support, or account management.
- Support platforms: Expenses related to help desk software, chatbots, and customer service management tools (e.g., Zendesk, Freshdesk).
Why Are Support Costs Significant?
Efficient customer support is integral to customer satisfaction and retention. A poor support system can lead to customer churn and negative reviews, which can harm a company’s reputation and profitability in the long term.
Licensing Fees and Royalties:
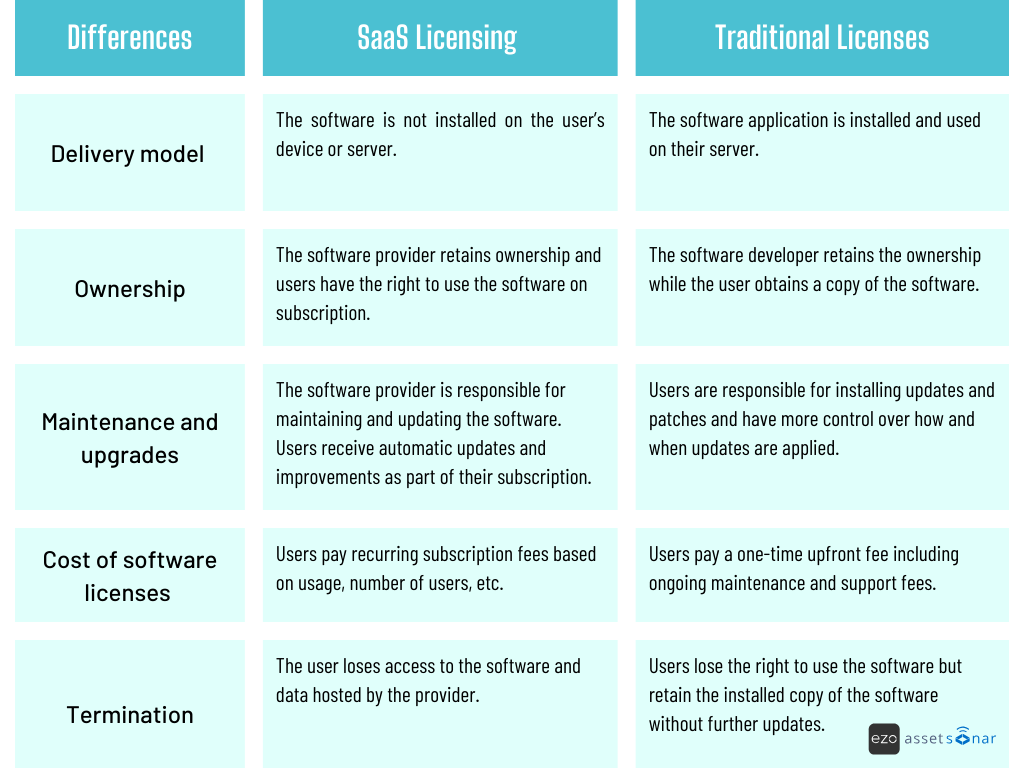
If a software company relies on third-party software, APIs, or libraries within its own products, the cost of licensing these tools is part of the cost of sales. Licensing fees can vary based on usage, the number of users, or the number of servers running the software.
- Third-party tools: Costs associated with integrating third-party libraries or software into the product.
- Royalty payments: If a portion of your software is licensed from another company, royalty fees are paid on a regular basis.
How Do These Costs Affect Profitability?
Licensing fees and royalties can be a substantial expense, especially if the software product relies on several external tools. Careful management of these costs and finding cost-effective alternatives can help in optimizing profitability.
Amortization of Software Development Costs:
For some software products, the development costs are capitalized and amortized over the software’s useful life. This means a portion of the development cost is allocated to each period based on the estimated lifespan of the product.
Why is Amortization Necessary?
Amortizing development costs ensures that large investments in software development don’t affect the profitability of a single accounting period. Instead, the cost is spread out over several periods to better match the revenue generated by the software.
Costs Associated with Software Deployment:
If the software requires regular updates, patches, or continuous deployment, the expenses related to this process are included in the cost of sales. This may include:
- Automated deployment tools: Costs for tools that automate the process of deploying software updates.
- API integration: Fees for integrating or maintaining third-party APIs, especially if they are essential for delivering the software to users.
How to Calculate the Cost of Sales for a Software Company:
The formula for calculating cost of sales remains relatively consistent across industries, but in the case of software companies, the key components differ. Here’s a basic formula for software companies:
java
Copy code
Cost of Sales = Development Costs + Infrastructure Costs + Support Costs + Licensing Fees + Amortization + Other Direct Costs
By accurately accounting for these components, software companies can determine their true cost of sales. This, in turn, enables them to evaluate gross profit and assess the overall profitability of their core operations.
Example Calculation:
Imagine a SaaS company with the following expenses for the fiscal year:
- Development Costs: $200,000
- Hosting and Infrastructure: $50,000
- Support Costs: $30,000
- Licensing Fees: $15,000
- Amortization of Development Costs: $10,000
The total cost of sales for the company would be:
bash
Copy code
$200,000 + $50,000 + $30,000 + $15,000 + $10,000 = $305,000
Also Read: Is Analytics A Good Minor To Go With Software Engineering – A Comprehensive Overview!
Cost of Sales vs. Operating Expenses:
It’s essential to distinguish between cost of sales and operating expenses. While the cost of sales includes the direct costs necessary to deliver a product or service, operating expenses cover the indirect costs of running the business. Operating expenses typically include:
- Marketing and advertising costs
- Administrative salaries
- Office rent
- General overheads
While both categories affect a company’s overall profitability, the cost of sales directly impacts gross profit, whereas operating expenses affect operating profit.
FAQ’s
1. What is the cost of sales in a software company?
Cost of sales refers to the direct expenses involved in producing, supporting, and delivering software products or services to customers.
2. How does cost of sales impact profitability?
Cost of sales directly affects gross profit; lower costs typically lead to higher profitability, as the business keeps more of its revenue.
3. What are the key components of cost of sales for software companies?
Key components include software development costs, infrastructure and hosting fees, customer support, licensing fees, and amortization of development costs.
4. How do software companies calculate the cost of sales?
The cost of sales is calculated by summing direct expenses like development, hosting, support, licensing, and other operational costs associated with delivering the software.
5. How is cost of sales different from operating expenses?
Cost of sales covers direct costs tied to product delivery, while operating expenses are the indirect costs of running the business, like marketing and administrative salaries.
Conclusion
The cost of sales for a software company includes direct expenses like development, hosting, support, and licensing fees. Managing these costs helps optimize profitability and improve pricing strategies. Tracking them provides insights into financial health and supports better decision-making.